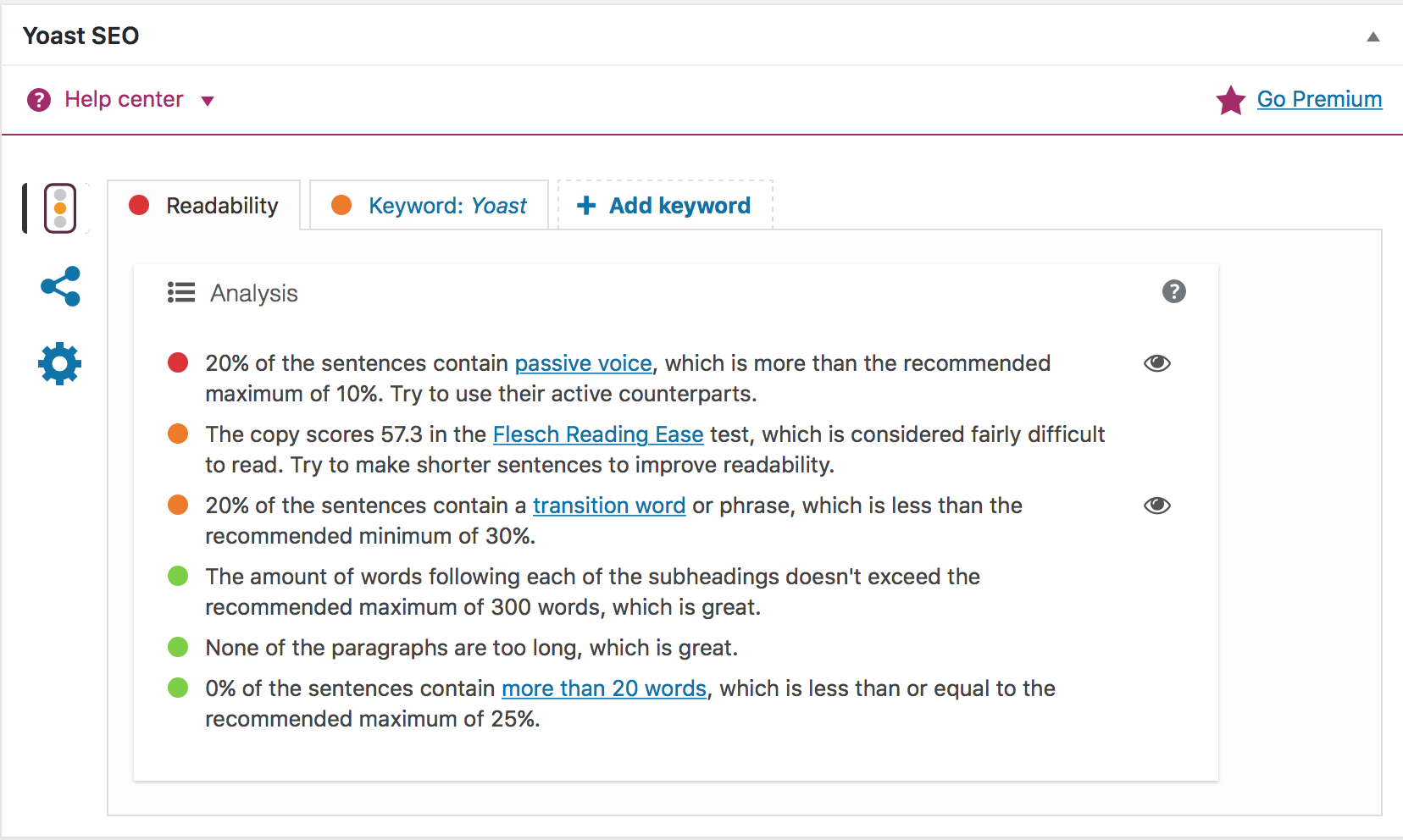
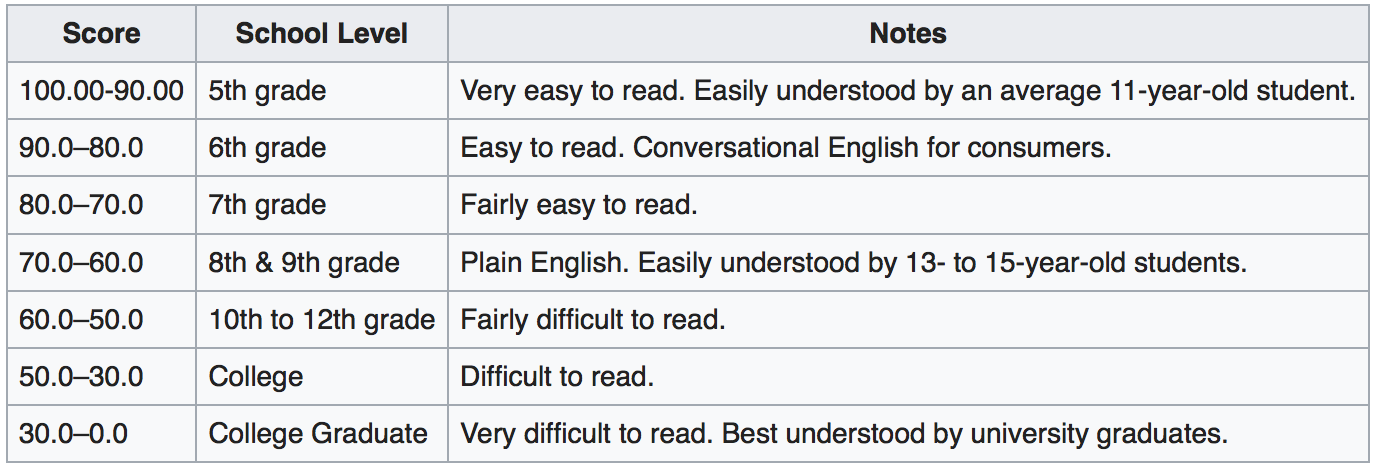
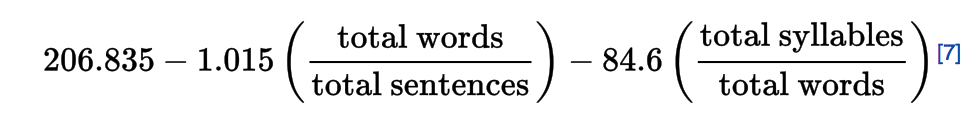Dear Readers,
In the last few posts, I explored freecodecamp.org, a non-profit that assists people in learning how to develop websites for free. I also show cased 10 quickly developed front-end prototypes. Why is free code camp awesome, it’s a free curriculum that prepares you for a Junior Web Developer role (Salary). It’s also great practice if you want to learn JavaScript, HTML and CSS. As a database engineer, I really wanted to learn more about these technologies as almost everything touches the web in some way. In this post, I will talk a bit more about backend-certificate and my current progress towards getting the certificate.

FreeCodeCamp.org provides 3 certificates. The first one is called the front-end certificate. It is the one that I would recommend starting with. It begins with very simple elements of a webpage like text, images and buttons. It then progresses through 200 lessons until you can develop TicTacToe and the Simon Game. The first 150 or so lessons will take the average person approximately 5 minutes each and so can be done during your daily commute (train). The remaining ones take significantly more time, but are well worth going through.
The next certificate I’m attempting is the backend certificate. Front-end development involves the actual webpage, the buttons, text and images that are presented in your browser. Front-end applications tend to utilize your computer and the resources tied to it. The backend certificate focuses more on sending and processing data stored on your a computer to your browser. Why would anyone want to store data on a separate computer, process it and send it to your web browser? First, you can process things in one location preventing a bunch of other computers from doing the work. This is the focus of cacheing. Second, you want a guarantee that your data doesn’t change, which is near impossible to do if you don’t have control of the computer. Third, you can take all this data and often aggregate it to look at interesting group behavior. These are just a few examples why you’d want a “backend” server.

The current curriculum focuses on a framework called Node.js. Node.js is written in JavaScript and is a framework for dealing with network connections. A good example of a network connection is going to your facebook profile and making a post. It involves, getting your profile page from a Facebook backend server called a http get request and then providing data to facebook in the form of your post called a http post request. Both these requests need to be handled by some form of network software, one to get your profile information and the other to store the new data in the database, permanent place for your data. Node.js specializes in handling these types of connections. In fact, it can handle hundreds of connections in a few seconds from many different people.
What other types of technology are covered and what would you learn from this curriculum:

npm – Node Package Manager, when you are dealing with websites there are a lot of moving pieces. You want to be able to set up node.js to handle connections. You also want to build logic around those connections, are you a bank processing credit card balances or is it just retrieving your blog post. NPM allows you to save a copy of that logic and makes useful logic available for others to use. It also provides a way to do automated tests. If you decide to for example change the functionality of your blog, you can run tests to see if it breaks your websites. Broken website often results in a blank page or missing elements. In the course, you do one whole module consisting of about 12 tasks that teach you how to manage your code.

node.js – Node as mentioned above is a library that deals with network connections. Many people use Node specifically for websites, but you can use it for other situations as well (maybe forwarding database connections). In this curriculum, there are two lessons that utilize node. One of the things you will end up building is a service where you type in a url with a date and it will convert it into different timezones. These backend services can of course become significantly more complicated.

express.js – Express is another JavaScript library, but focuses more on building websites. Express.js would set up for example a template of how a Facebook profile would look like (Picture on the top left, a background picture, short summary and posts below) and bind it to a specific url. It would also create separate urls for your facebook profile vs your activity feed. The lessons focus on very simple webpages and templating.

mongodb – mongodb is a database and is not written in JavaScript. It focuses on storing data on the backend server and is optimized for quick retrieval. Mongo itself is called a document store, which means that it does not store things in tables like a spreadsheet, but rather as a set of keys and collections. One neat thing about this is that you can store a set of collections within a collection, which makes it very flexible. An example of this type of data can be seen here (it is called JSON):
Example Google Maps JSON File
MongoDB section has about a dozen tasks and focuses on storing data, retrieving it and using it in a web application. This is important in that you can retrieve the data for a specific person and just put it in a template (or webpage). Hence, your name, summary and posts in facebook are all stored in the database and are unique to the individual (database like Mongo), but are presented in the same way as a profile page (node.js/express.js provide template and logic).
In the next few posts, I will talk about the second part of the backend certificate, which are the 10 projects that utilize the tutorials mentioned previously to produce products people can use. After doing those 10 projects, a person at freecodecamp.org could potentially develop backends similar to quora.com or facebook.com. One thing to note, even though that website would look similar to facebook, it would be missing the messaging and not operate at the scale of Facebook. Handling webpages for billions of users is a much harder problem.
Best,
Chris